Skin fungus, also called fungal skin infection, is one of the most common skin problems worldwide. Among them, ringworm is the best-known form, often showing up as red, itchy patches that can spread quickly if untreated.
This guide explains what skin fungus and ringworm are, how they spread, the best medical and natural treatments, and practical steps to prevent them.
RELATED:Natural Remedies for Healthy Veins and Skin
1. What Are Skin Fungi?
Fungi are tiny microorganisms that naturally live on the skin, hair, and nails. Normally, they don’t cause harm, but in warm and moist environments, they can grow out of control and trigger infection.
Common types of fungal skin infections include:
- Ringworm (Dermatophytosis): Caused by dermatophytes. Depending on the body part affected, it has different names.
- Cutaneous Candidiasis: Caused by Candida albicans, often found in moist folds such as armpits, groin, and between fingers.
- Onychomycosis: Fungal nail infection that makes nails thick, brittle, or discolored.
- Pityriasis Versicolor: Caused by Malassezia, leading to lighter or darker skin patches.
2. What Is Ringworm?
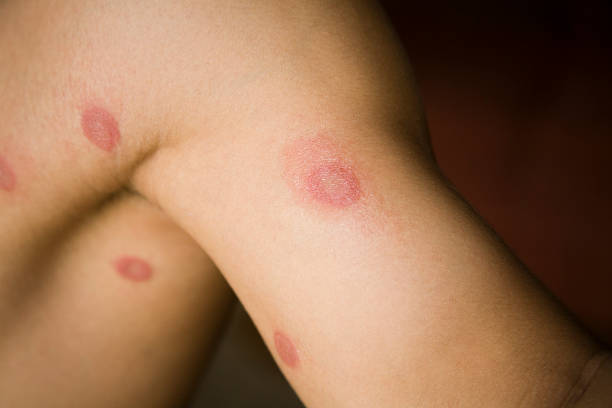
Ringworm is a surface-level fungal infection caused by dermatophytes. It often looks like a red, circular rash with raised edges and sometimes scaly skin.
Types of Ringworm and Key Symptoms
-
Tinea Corporis (Body Ringworm):
- Found on arms, legs, or torso.
- Red circular patches with a clear center.
- Causes itching and irritation.
-
Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm):
- Appears on the scalp, sometimes causing hair loss.
- May cause severe dandruff or crusting.
- More common in children.
-
Tinea Pedis (Athlete’s Foot):
- Between toes and soles of feet.
- Causes scaling, cracking, and unpleasant odor.
-
Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris):
- Affects groin and inner thighs.
- Itchy, red, and scaly patches.
-
Tinea Unguium (Onychomycosis):
- Attacks the nails, making them brittle and thick.
- May cause discoloration or deformation.
3. How Do Fungi Spread?
Fungal infections are contagious and spread through:
- Direct skin contact with infected people.
- Contact with infected animals (dogs, cats, horses).
- Shared items like towels, combs, clothing, or shoes.
- Damp public places such as swimming pools, gyms, or showers.
Risk factors: Excessive sweating, tight clothing, and poor hygiene.
4. Medical Treatments for Skin Fungus and Ringworm
Treatment depends on the type and severity of infection.
A) Topical Antifungals (Creams and Ointments)
For mild infections, doctors recommend creams applied twice daily for 2–4 weeks, including:
- Clotrimazole (Canesten)
- Miconazole (Daktarin)
- Terbinafine (Lamisil)
- Ketoconazole (Nizoral)
B) Oral Antifungals
For widespread or stubborn infections, oral antifungal pills may be prescribed:
- Itraconazole
- Fluconazole
- Terbinafine
These require a prescription and can last several weeks to months.
C) Specific Treatments
- Onychomycosis: Antifungal nail lacquers (amorolfine) or long-term oral antifungals.
- Tinea Capitis: Oral griseofulvin or terbinafine is most effective.
5. Natural Remedies for Skin Fungus
Home remedies can ease symptoms and support medical treatment, but they should not replace prescription antifungals.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Dab with cotton twice daily.
- Garlic: Mix crushed garlic with coconut oil, apply for 30 minutes, then rinse.
- Tea Tree Oil: Dilute in coconut oil and apply twice daily.
- Baking Soda: Apply as a paste on skin or sprinkle in shoes.
- Aloe Vera: Apply fresh gel three times daily to soothe and heal.
RELATED:Cucumbers: Health Benefits and Hidden Risks
6. How to Prevent Skin Fungus and Ringworm
- Keep Skin Dry and Clean: Dry thoroughly after showers, wear cotton clothing, avoid tight synthetic fabrics.
- Avoid Sharing Items: Don’t share towels, clothing, or grooming tools. Wash infected fabrics in hot water.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Use sandals in public showers, pools, or gyms. Change socks daily and wear breathable shoes.
- Boost Your Immune System: Eat nutrient-rich foods, get enough rest, and reduce stress.
- Use Antifungal Powders: Especially on feet to stay dry.
Conclusion
Skin fungus and ringworm are very common but highly treatable. With consistent use of antifungal creams, oral medications when needed, and complementary natural remedies, infections can be eliminated.
Prevention matters most: good hygiene, keeping skin dry, and strengthening your immune system will greatly lower your risk. If symptoms continue or worsen, see a dermatologist for proper care.
Taking care of your skin today helps you stay fungus-free tomorrow.




